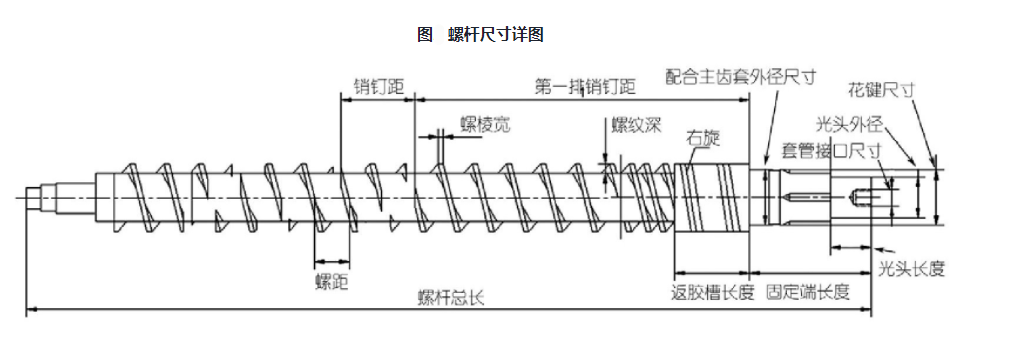
HOT PROD UCT

HOT PROUDCT
WELCOME TO
ZHOUSHAN XINLU PLASTICS MACHINERY CO., LTD.
Zhoushan Xinlu is a professional OEM & OD of screw and barrels for extrusion and injection molding machines who provide high-quality & competitive burst-sales single and twin screw barrel economically and efficiently for nearly16 years!
At present,we produce high-quality series screw and barrel products such as filmblow, waste recycling granulation, extrusion pipe,plate, super-large parallel twin screw conical twin screw, micro-medical instrument screw barrel, food processing screw, and so on, which have received many favorable comments.
We must deal with and solve the various needs of clients in terms of quality, price,delivery time and after-sales service to seek for long-term partners. XINLU welcome to cooperate with you!
LATESTT NEWS
Repair of the barrel
The inner surface hardness of the barrel is higher than that of the screw, and its damage comes later than that of the screw. The scrap of the barrel is the increase of the inner diameter due to time wear. Its repair method is as follows:
1, due to wear to increase the diameter of the barrel, if there is a certain nitriding layer, the barrel hole can be directly boring, grinding to a new diameter size, and then prepare a new screw according to this diameter.
2. The inner diameter of the barrel is machined and trimmed, and the alloy is cast again, the thickness is between 1~2mm, and then finished to the size.
3, under normal circumstances, the homogenization section of the barrel wear faster, this section (take 5~7D length) can be boring and trimmed, and then equipped with a nitriding alloy steel bushing, the diameter of the inner hole is referred to the diameter of the screw, left in the normal matching gap, processing and preparation.
It is emphasized here that the two important parts of the screw and the barrel, one is a slender threaded rod, and the other is a small and long hole in diameter, their machining and heat treatment processes are more complex, and the guarantee of accuracy is more difficult. Therefore, whether to repair or replace the new parts after wear of these two parts must be comprehensively analyzed from an economic point of view. If the repair cost is lower than the cost of replacing the new screw, it is decided to repair, this is not necessarily the right choice, and the comparison between the repair cost and the renewal cost is only one aspect. In addition, it also depends on the ratio of the repair cost and the time of using the screw after repair to the renewal cost and the use time of updating the screw. It is the right choice to adopt the scheme with small ratio only economically.
Conical twin screw extruder and wear failure repair methods extruder wear failure after depending on the screw and barrel wear degree and repair symptoms can adopt the following methods:
- by measuring the screw and barrel of wear in 0.30 Within the mm range, the screw and barrel can be chrome-plated and then finely ground and polished by a dedicated grinding machine to meet the original fit size indicators.
(2) when the barrel when the wear and tear of the available special machine tools will be broaching machine barrel, the other processing a cylinder liner, take hot pressing method and the original barrel set set as a whole, and then according to the size of cylinder diameter (usually slightly smaller than the original barrel diameter size), finishing the other new screw, make it to suit the new cylinder diameter.
(3) update the screw and barrel. It is best to purchase from the original extruder manufacturer to prevent the newly purchased screw and barrel from not matching the electric heating ring, bracket and spline sleeve of the original extruder. Of course, for the general extruder user enterprises, the above-mentioned repair methods require certain mechanical processing equipment and capabilities. The vast majority of enterprises do not have these capabilities and need to contact professional extruder equipment manufacturing enterprises to entrust the repair.
引自-韦永斌.影响锥形双螺杆挤出机磨损的因素及延缓磨损的对策[J].技术与市场,2011,18(11):41-44.
Conical twin-screw installation
Conical double screw to install bite together of the conical twin-screw see below. The installation of conical twin-screws and parallel twin-screws is not quite the same. Since the conical twin-screw has a taper, it can only be installed from the back of the screw barrel. First, remove the special tool for the screw barrel. Then, correctly engage the conical twin-screw and place it into the screw barrel. Connect it to the output shaft on the gearbox according to the position on the coupling, and then lock the screw barrel. It is ideal to control the gap of the conical twin-screw within 0.2mm, just like that of the parallel twin-screw. The gap between the conical twin-screw and the barrel is adjustable and can be appropriately adjusted according to the plasticization condition of the material. Due to the differences in design concepts among various extruder manufacturers, the specific gaps should refer to the instruction manual of the extruder.
引自-陈少敏.挤出机螺杆对PVC型材生产的影响[J].聚氯乙烯,2013,41(03):25-26+34.
Disassembly and Assembly Process of the Screw
(1)Open the machine head and extrude the material in the extruder. After the material is completely extruded, keep the screw idling for at least 5 minutes to prevent residual material inside the screw from affecting screw removal.
(2)Remove the pressure sensor from the machine head and open the side pressure roller simultaneously.
(3)Remove the pins of the extruder: Each pin on the extruder is locked with a clamping nut. Follow these steps for removal: ① Use a hex wrench to remove the nut; ② Screw the pin puller into the pin, then use the pin extractor to remove the pin; ③ Continuously strike the rear end of the pin puller with a sliding sleeve to overcome the pin’s fastening force. Repeat this action until the pin is pulled out. Note: Do not pull the pin extractor toward your body during removal. Sudden pin extraction may cause injury to the operator. Keep a record of the pin arrangement during removal to provide a theoretical basis for pin installation or process problem-solving.
(4)After confirming all pins are removed, disassemble the screw casing, insert the screw ejector, and use the ejector’s threads to push out the screw. Once the splines of the screw are fully disengaged from the extruder, pull the screw out from the machine head. If resistance is significant, extend the inner casing and continue using the screw ejector. For angled screws (especially plunge-type screws), secure a lifting rope to the screw head during ejection to prevent accidental sliding and injury.
(5)After pulling out the screw, inspect the wear of the screw washer and the mating part with the main gear sleeve. Replace them if necessary.
(6)For a new screw, apply grease to the splines and high-temperature anti-seize oil to the smooth ends. Do not forget to install the screw washer, then carefully slide the screw into the extruder from the machine head side.
(7)Slide the screw’s splines into the spline sleeve of the speed reducer until the screw contacts the front end face of the drive shaft. When assembling the splines, manually rotate the coupling to ensure the screw’s splines smoothly enter the spline sleeve of the output shaft, avoiding local upsetting (i.e., collision) of the spline teeth and the sleeve teeth. If resistance is encountered during installation, identify the cause and eliminate it without using external force. Do not strike the screw. If striking is necessary, first push the screw as far as possible into the drive shaft’s spline sleeve before applying force.
(8)After inserting the screw, use a casing to tension it. Check whether the position of the screw’s blade aligns with the pin groove to ensure each inserted pin does not collide with the screw.
(9)Install the pins according to the pre-recorded pin arrangement diagram and reconnect the screw casing. Note: Ensure the screw casing is well-sealed to prevent water leakage.
(10) Manually rotate the coupling for at least one full revolution to check for significant resistance.
(11)Install the rotary joint and coupling guard.
(12)Close the side pressure roller of the feed seat.
(13) Install the temperature sensor.
引自-顾建.挤出机螺杆拆装难点及解决方法浅析[J].
1.1 Thermal Spraying Repair
Thermal spraying offers surface strengthening for repairs, characterized by high-quality wear-resistant coatings, low cost, high efficiency, and wide applicability. Its basic process involves: melting spraying materials (metals, ceramics, plastics, etc.) into a liquid or molten state, refining them into particles ranging from tens to hundreds of microns, and spraying these particles onto the base material to form a coating.
For example, stainless steel corrosion-resistant steel powder is often used to spray the screws of single-screw plastic extruders for PVC processing. The sprayed coating consists of rapidly quenched particles, which exhibit high hardness. During spraying, a supersaturated alloy state and an oxide film form, further increasing the coating’s hardness—beneficial for enhancing wear resistance. To ensure coating properties and quality, porosity must be controlled by maximizing particle temperature and spraying speed.
Key process parameters for thermal spraying:
Heat Source: Flame spraying typically uses acetylene as fuel, with a temperature of ~3,100°C; arc spraying reaches 5,538–6,649°C; plasma spraying achieves up to 11,093°C. Plasma spraying is optimal for rapid heating and particle transport, followed by arc spraying and oxy-acetylene flame spraying.
Spraying Material: For arc and flame spraying, the diameter of the metal wire must match the heat source power to obtain the best coating.
Spraying Distance: This refers to the distance between the spray gun and the workpiece. Typical values: 100–200 mm for flame spraying, 50–100 mm for plasma spraying, and 180–200 mm for arc spraying.
Spraying Angle: The angle between the central axis of the spray jet and the substrate surface should ideally be 90°, but must not exceed 45° to avoid shadowing effects.
1.2 Chrome Plating
Chrome plating layers exhibit excellent wear resistance, anti-friction, and corrosion resistance, significantly improving the quality of repaired parts—particularly surface wear resistance.
1.3 Cladding Repair
Vacuum fusion alloy coating technology is a modern surface metallurgy technique that modifies the composition and structure of the substrate’s working surface to meet requirements for wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. The process occurs under vacuum: concentrated heat melts a pre-applied alloy coating on the substrate surface, allowing it to infiltrate the substrate. Upon cooling, the coating and molten zone recrystallize, forming a strong bond with the substrate. This entire process of melting, infiltration, diffusion, intersolution, and recrystallization constitutes a surface metallurgical reaction.
引自-朱玉明.双螺杆挤出机螺杆机筒的耐磨处理和修复[J].科教文汇(下旬刊),2015,(24):180-181.
Main cause of wear of the screw extruder
The normal wear of the screw and cylinder of the screw extruder mainly occurs in the feeding area and the metering area. The main wear reason is caused by the dry friction between the slice particles and the metal surface, and the wear is reduced.
Screw and cylinder abnormal wear will occur in the screw knot and foreign body stuck, ring refers to the screw condensation material, if the screw extruder lack of good protection device, powerful driving force may twist the screw, stuck will produce extraordinary huge resistance, causing serious damage on the surface of the screw and barrel serious scratches, barrel scratch is difficult to repair.
From the design principle, the service life of the cylinder is longer than the screw. For the normal wear of the cylinder, it is generally no longer repaired. The method of repairing the screw thread is often used to restore the radial clearance between the inner hole of the cylinder and the outer diameter of the screw.
Solution to screw wear
The local damage of screw thread is repaired by overwelding special abrasion anticorrosion alloy. Inert gas protective welding and plasma argon arc welding are generally used, and metal spraying technology can also be used for repair.
First, the surface of the worn screw is ground to a depth of about 1. 5 mm, and then the alloy layer is welded to sufficient size to ensure sufficient processing allowance. Finally, the outer size of the outer circle of the screw and the side of the screw to the screw are the original size.
引自-沈兵.螺杆挤出机的维护保养要点[J].聚酯工业,2011,24(06):49-51.